This volume is considered to be 30 of. Anatomic dead space is the volume of gas within the conducting zone as opposed to the transitional and respiratory zones and.
Effects Of Positive Pressure Ventilation On Pulmonary Physiology Deranged Physiology
Dead space is the volume of a breath that does not participate in gas exchange.

What is dead space ventilation. Physiologic or total dead space is the sum of anatomic dead space and alveolar dead space. To get the true minute ventilation the dead space ventilation VD and the alveolar ventilation VA must be added together VE VDanat VA. Physiologic dead space is calculated by Bohrs equation which assumes that 1 all of the CO2 in expired air comes from functional alveoli alveoli that are perfused.
The inspired air is humidified brought to the body temperature and filtered during its passage through the dead space. Generally physiological dead space has two components. Physiological dead space may be increased with lung disease due to an increase in the alveolar component.
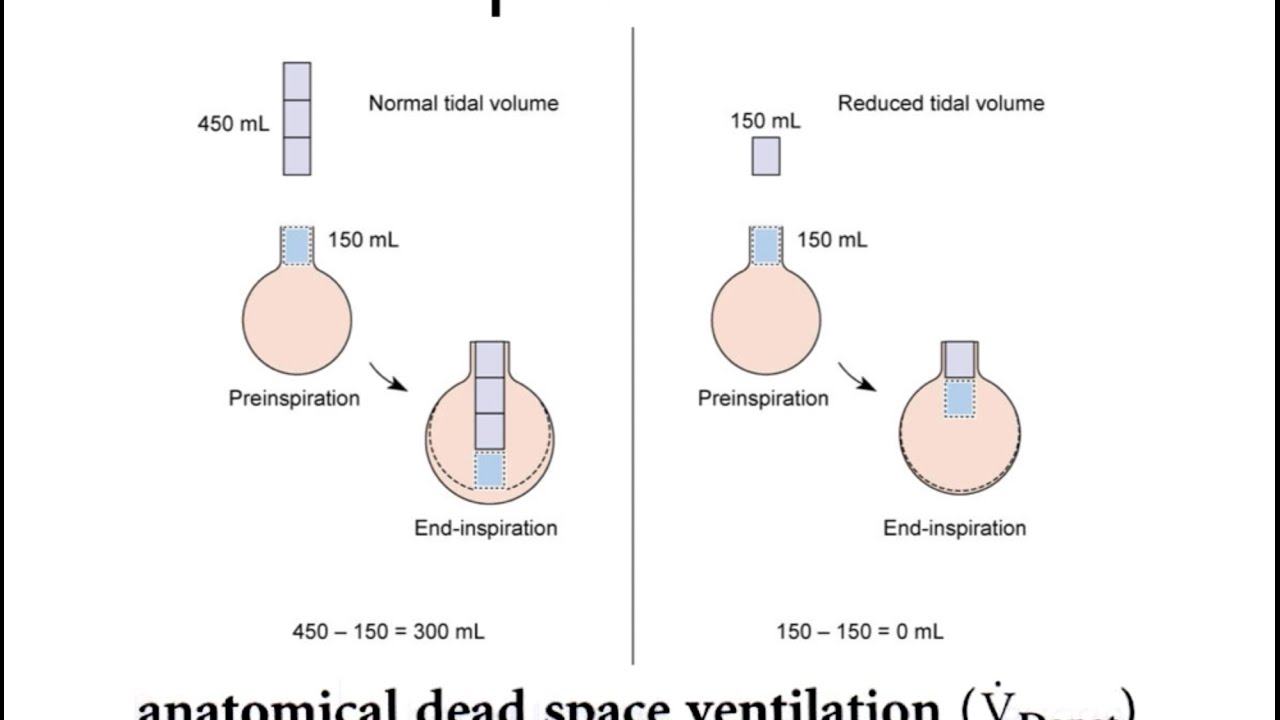
Minute ventilation is the volume of air entering or leaving the lung each minute which includes alveolar ventilation and dead space ventilation. The next figure shows that with a constant alveolar ventilation it is possible to reduce the respiratory rate with constant tidal volume or to decrease the tidal volume with constant respiratory rate very substantially. Hypovolemia hypotension and dead space ventilation This is the most common cause of hypoxemia in the perianesthetic period.
It is determined by subtracting the dead space volume from the tidal volume and multiplying the result by the respiratory rate. Alveolar ventilation Resp rate tidal volume - dead space In short alveolar ventilation is the volume of. Anatomical dead space and alveolar dead space.
This means that there is adequate ventilation but inadequate perfusion otherwise known as dead space. Anatomical dead space is represented by the volume of air that fills the conducting zone of respiration made up by the nose trachea and bronchi. It is ventilation without perfusion.
The current calculation of physiological dead space utilising measurements of arterial CO 2 tension P aCO 2 and mixed expired CO 2 tension P ECO 2 was initially thought to include an anatomical dead space representing the fraction of ventilation advancing no further than the conducting airways and an alveolar dead space representing. Physiological dead space. Physiological dead space VDPhys is the total dead space.
Hypoxemia will occur if there is a problem with a fresh blood supply moving past the alveoli within the pulmonary vasculature in the lungs. It is a function of the size of the tidal volume the rate of ventilation and the amount of dead space present in the respiratory system. On expiration the air in the dead.
The two types of dead space are anatomical dead space and physiologic dead space. VD is physiologic dead space ml VT is tidal volume PaCO2 is the PCO2 of arterial blood and PECO2 is the PCO2 of expired air. The movement of air into and out of the alveoli.
Alveolar dead space VDAnat is the total volume of the ventilated alveoli that are unable to take part in gas exchange due to insufficient perfusion ie. 2 that inspired air has no CO2 and 3 that alveolar and arterial PCO2 are equal. The anatomical dead space can be reduced by 50 by tracheostomy which is beneficial for patients with weak respiration and diminished tidal volume.
This means that there is inadequate ventilation but adequate perfusion otherwise known as a shunt. This can happen when tidal volume TV is reduced and the. Dead space represents the volume of ventilated air that does not participate in gas exchange.
Some of the air a person breathes never reaches the gas exchange areas but simply fills respiratory passages where gas exchange does not occur such as the nose pharynx and trachea. This is a perfect way of wording it because takes into account the usual proportional relationship of dead space and minute ventilation where. The term wasted ventilation has been proposed as an alternative which sounds less technical but is certainly more accurate3.
Atelectasis is defined as the collapse of part or all of the lungs. The volume of air that participates in gas exchange because it is in contact with perfused alveoli is the alveolar ventilation V A V E V D physiologicalThe alveolar ventilation is critical as it determines the amount of air presented to alveoli into which CO 2. We determined if there were differences in dead space and alveolar ventilation in ventilated infants with pulmonary disease or no respiratory morbidity.
Physiological dead space VDphys is another term that is troublesome but is commonly used in the literature. Due to VQ mismatch. Dead space is the fraction of tidal volume which does not participate in gas exchange.
In other words th of the tidal ventilation will remain in the dead space. Physiologic dead space volume 35 to 525 mlkg makes up about 35 of this tidal volume 34 while the remainder of the tidal volume 65 to 975 mlkg is the portion of the tidal volume that actually participates in gas exchange alveolar ventilation volume. Impact of dead space reduction.
Dead space is the volume not taking part in gas exchange and if increased could affect alveolar ventilation if there is too low a delivered volume. A cumulative measure of wasted ventilation. Dead space total dead space or physiologic dead space is the second contributor to the ventilation-perfusion mismatch.
The previous figures showed the impact of the dead space on alveolar ventilation CO 2 clearance. This air is called dead space air because it is not useful for gas exchange. Dead Space and Its Effect on Alveolar Ventilation.
That is the sum of anatomical and alveolar dead space.
Physiologic Dead Space Ventilation Rates Physiology Flashcards Draw It To Know It

Respiratory Physiology Knowledge Amboss

Anatomic And Physiologic Dead Space Osmosis

Relations Between Dead Space Respiratory Rate Tidal Volume And Alveolar Ventilation Impact Of Protective Ventilation Settings And Impact Of Instrumental Dead Space Part 2

Ventilatory Response To Exercise In Cardiopulmonary Disease The Role Of Chemosensitivity And Dead Space European Respiratory Society

Schematic Representation Of Three Compartment Lung Model Showing Download Scientific Diagram

Alveolar Ventilation Perfusion Key Points Alveolar Ventilationv A

Basics Of Dead Space Ventilation Criticalcarenow

Pulmonary Shunt Dead Space Ventilation Allnurses Pulmonary Shunt Respiratory Therapy Student Respiratory Therapist Student

The 3 Compartment Lung Model Described By Riley 36 37 Represents Gas Download Scientific Diagram
20170303 Clinical Problems And Evaluation Of Ventilation And Dead Space Youtube

Litica Diktatura Kockanje Dead Space Ventilation Riverkwaibridgeresort Net

Ventilation Perfusion Mismatch The Airway Jedi Dead Space Vs Shunt

Dead Space And Its Components Deranged Physiology

Dead Space The Physiology Of Wasted Ventilation European Respiratory Society

Anatomic And Physiologic Dead Space Osmosis

Post a Comment
Post a Comment